Traditionally, flow cytometry has been used to identify distinct cell types within a heterogeneous pool of cells, based on extracellular or surface marker expression, an application commonly known as immuno-phenotyping. However, this technology is also readily amenable to intracellular target detection and can be successfully applied to the study of complex signaling events.
Thus, when combined with the detection of cell surface markers intracellular flow cytometry becomes a powerful platform, which enables characterization of signaling networks at a single cell level within phenotypically distinct cell populations.
Advantages of Intracellular Signaling Analysis Using Flow Cytometry
- Multi-parameter (e.g., multiple intra- and extra-cellular targets, viability, DNA content, cytokine profile, etc.)
- Sensitivity (single cell analysis)
- Quantitative output
- High throughput (up to a 1000 cells/sec can be processed)
- Fast readout (min to hours to generate data)
Check out the video below to see how it works...
Video Transcript
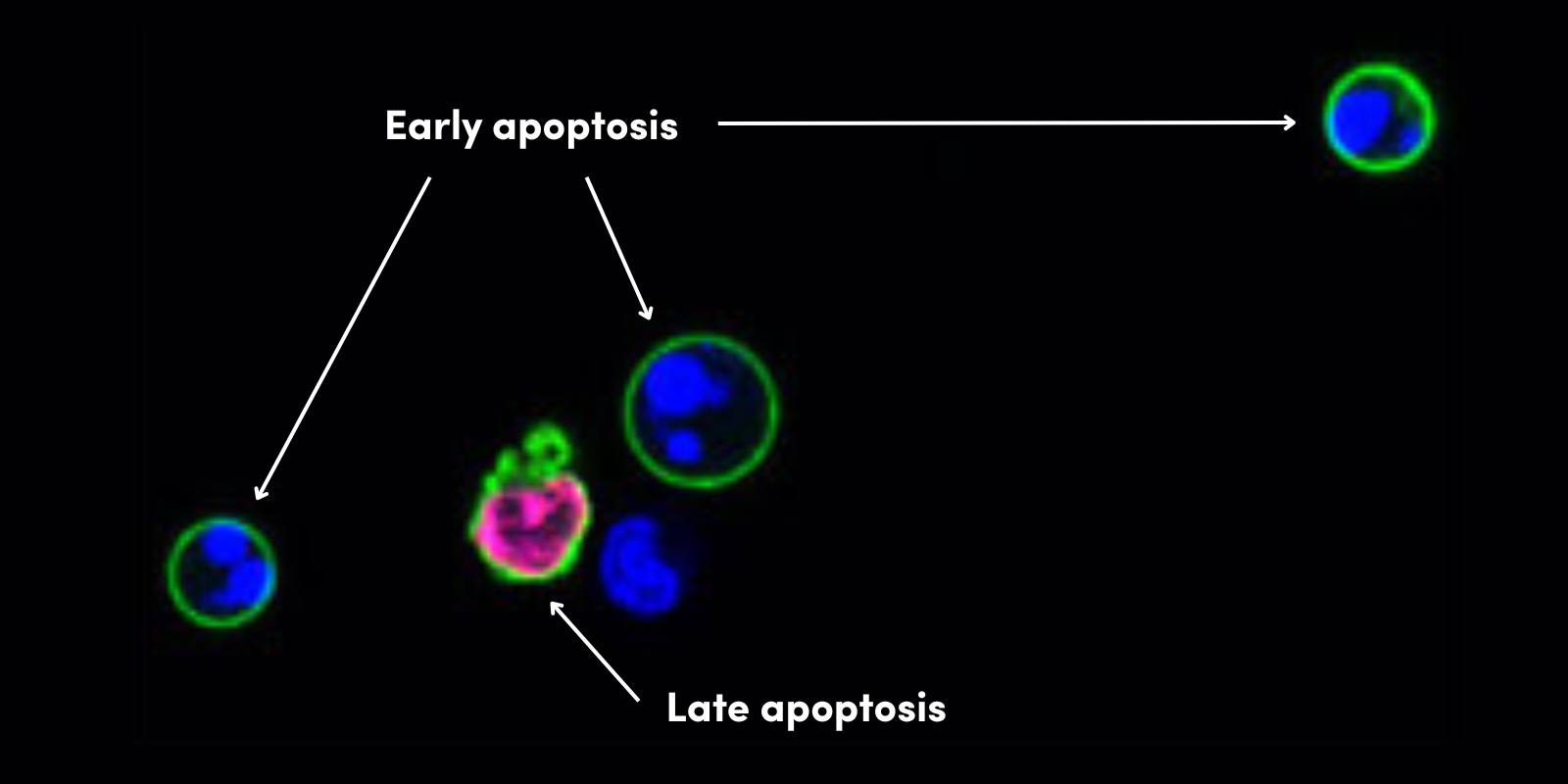
Cell processes are controlled by complex and dynamic intracellular signaling networks. Surface receptors pass information into the cell by modifying cytoplasmic proteins. These modifications include phosphorylation, methylation, and acetylation, which control a broad range of cellular functions, including growth, development, and apoptosis. Disruption of signaling networks often leads to disease.
To understand signaling processes in normal and pathological conditions, identification and quantification of signaling proteins is necessary. Flow cytometry is ideal for such a task. Flow cytometry is a laser-based technology widely used to phenotype cells using antibodies directed against surface markers. It can also allow simultaneous analysis of multiple intracellular targets using antibodies that detect signaling proteins, their post-translational modifications, epigenetic modifications, and downstream transcription factors.
The first step of intracellular flow cytometry is fixation of the cells using formaldehyde, which immobilizes proteins and preserves transient signaling events. Cells are then permeabilized with methanol or detergent, allowing antibodies to access to the intracellular space. Optimal fixation and permeabilization conditions depend on the location and biochemistry of the target epitopes, which should be carefully considered to ensure successful antigen detection, especially when staining surface and intracellular proteins simultaneously. Since multiple signaling proteins and surface antigens can be identified using fluorescently distinct antibodies, flow cytometry can readily characterize signaling profiles at the single-cell level within phenotypically distinct populations.
This allows the characterization of the relationship between intracellular targets, and enables detection of signaling events from rare cell populations within a heterogeneous sample. Multiplex analysis of these proteins targets saves time and resources, while producing data-rich results, making intracellular flow cytometry an invaluable tool to unravel the complexities of cell signaling. For more information on validated products and optimized protocols for flow cytometry, visit www.cellsignal.com/flowcytometry