Viability dyes are widely used when counting and passaging cells, assessing chemical toxicity, and performing flow cytometry experiments because they allow one to distinguish living cells from dead or dying cells. They are frequently used in flow cytometry to improve data quality, where inclusion of dead cells in the analysis may skew experimental results.
How Do Viability Dyes work?
The biology of a live, healthy cell is different from that of a dead or dying cell. Additionally, even if the biology of a particular target or pathway of interest is not disrupted, antibodies often exhibit high degrees of nonspecific binding in dead cells, hindering reliable analysis. Excluding dead and dying cells from your analysis is critical to ensure your data are accurate and reproducible.
Non-Fixable Cell Viability Dyes
The most commonly used viability dyes are DNA-intercalating dyes that interact with nucleic acids. They are not able to cross an intact plasma membrane and thus are excluded from live cells, which will not be labeled, whereas dead cells will be brightly stained (Figure 1).
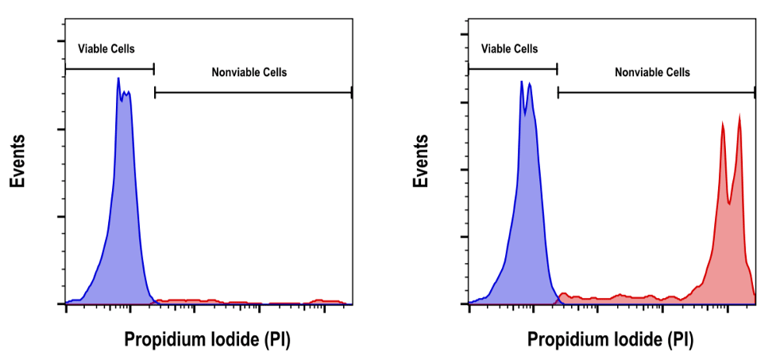
Figure 1. Propidium iodide staining profiles. Example of healthy Jurkat cells (left) and a mixed population of viable and nonviable Jurkat cells (right) stained with Propidium Iodide (PI)/RNase Staining Solution #4087.
Some examples of dyes with different excitation/emission profiles include propidium iodide (PI), 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD), and DRAQ7™. While these dyes are useful for live cell experiments, if an experiment requires fixing and/or permeabilizing cells, these dyes will diffuse out of the dead cells and wash away, limiting their utility.
While the DNA-intercalating dyes enable negative selection of viable cells, there are also a variety of dyes that can be used for positive selection of viable cells. Although these use different mechanisms to specifically label viable cells, they typically rely on standard metabolic processes to do so. One commonly used dye for positive selection of live cells, calcein AM, is a non-fluorescent intermediate that can cross intact cell membranes. Calcein AM forms a fluorescent product, calcein, in viable cells when acted on by intracellular esterases. Unlike calcein AM, calcein is not membrane-permeable, so it cannot escape by diffusing across the plasma membrane. Since calcein is retained within viable cells, these cells will fluoresce.
Fixable Cell Viability Dyes
Amine-reactive dyes are another class of viability dye. Like the DNA-intercalating dyes, they brightly label dead cells, but unlike the DNA-intercalating dyes, they covalently bind their targets, allowing users to fix and/or permeabilize cells without losing signal. Although all cells are technically dead once fixed and permeabilized, using an amine-reactive dye beforehand, such as a Ghost Dye™ from CST, lets researchers segregate cells that were alive from cells that were dead at the time the entire population was fixed. Amine-reactive dyes will also label live cells, since a small fraction of any given cell's amine-reactive groups are available extracellularly. Non-viable cells with loss of membrane integrity will react with significantly more dye than healthy cells in the same sample. These non-viable cells, which will be most brightly labeled, can be excluded from analysis. Figure 2. Ghost Dye™ Violet 450 staining profile. Live and fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were combined and stained with Ghost Dye™ Violet 450 Viability Dye #49826.
Figure 2. Ghost Dye™ Violet 450 staining profile. Live and fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were combined and stained with Ghost Dye™ Violet 450 Viability Dye #49826.
How to Use Viability Dyes in Flow Cytometry Experiments
When using a DNA-intercalating dye or an amine-reactive dye, nonviable cells will display bright signal in the dye’s emission channel; be sure to exclude this population from your analysis. If using a positive selection dye, the live cells will display positive staining, so the negative cells should be excluded from downstream analysis.
Viability dyes offer a simple way to improve confidence in your data—most require only a short incubation period to enable the separation of live and dead cells. As always, the best practice is to consult the manufacturer's recommended protocol when incorporating a viability dye into your experiment.
Explore CST Ghost Dyes, which are available in a variety of colors, allowing you to select the dye that fits best in your multiplex antibody panel.