The use of multiple antibodies in a single experiment can provide useful information to researchers. Co-staining with multiple antibodies and cellular dyes is a simple, low-content form of multiplex analysis. Techniques for performing multiplex analyses in cells and tissues are powerful research tools that are applicable to general cell biology studies as well as diagnostic purposes. These techniques allow researchers to detect multiple biomarkers to assess their samples. They also allow for easy colocalization studies to determine relationships between analytes.
Here, we describe two common techniques for immunofluorescent (IF) staining using multiple antibodies in the same assay.
Indirect IF Protocol Using Antibodies Raised in Different Species
Below is a general protocol overview for indirect IF using antibodies raised in different host species (for example, rabbit and mouse). Note that the actual protocol will vary based on the specific products’ recommended protocol.
- Fixation / permeabilization
- Optimize protocol for best results with both antibodies
- Separate testing may be required
- Rinse
- Block cells to avoid non-specific binding of the secondary antibody
- Most efficient if both secondaries raised in the same species (i.e., goat)
- Dilute each primary antibody to its recommended dilution in antibody dilution buffer; incubate overnight at 4°C
- Rinse
- Dilute each fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibody to its recommended dilution in antibody dilution buffer; incubate for 1hr at RT
- Secondary antibodies must be conjugated to fluorophores without spectral overlap
- Perform any counterstaining steps using complementary reagents, mount in antifade reagent
The pros and cons of using an indirect method of IF staining and antibodies raised in different host species are as follows:
Pros:
- Brighter than direct detection using conjugates
- Similar to standard staining protocols (Immunofluorescence Protocol with Formaldehyde Fixation)
- Utilizes common reagents and doesn’t require special imaging equipment
Cons:
- Limited by available host species
- Requires separate secondary incubation step
 Left: SNB19 cells stained using α-Parvin (D7F9) XP® Rabbit mAb #8190 detected with Anti-rabbit IgG (H+L), F(ab')2 Fragment (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) #4412 (green), Lamin A/C (4C11) Mouse mAb #4777 detected with Anti-mouse IgG (H+L), F(ab')2 Fragment (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) #4409 (red), and DRAQ5® #4084 (blue pseudocolor).
Left: SNB19 cells stained using α-Parvin (D7F9) XP® Rabbit mAb #8190 detected with Anti-rabbit IgG (H+L), F(ab')2 Fragment (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) #4412 (green), Lamin A/C (4C11) Mouse mAb #4777 detected with Anti-mouse IgG (H+L), F(ab')2 Fragment (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) #4409 (red), and DRAQ5® #4084 (blue pseudocolor).
Center: MCF-7 cells stained using AIF (D39D2) XP® Rabbit mAb #5318 detected with Anti-rabbit IgG (H+L), F(ab')2 Fragment (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) #4412 (green), EpCAM (VU1D9) Mouse mAb #2929 detected with Anti-mouse IgG (H+L), F(ab')2 Fragment (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) #4409 (red), and DRAQ5® #4084 (blue pseudocolor).
Right: MCF-7 cells stained using Caveolin-1 (D46G3) XP® Rabbit mAb #3267 detected with Anti-rabbit IgG (H+L), F(ab')2 Fragment (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) #4412 (green), Ki-67 (8D5) Mouse mAb #9449 detected with Anti-mouse IgG (H+L), F(ab')2 Fragment (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) #4409 (red) and DRAQ5® #4084 (blue pseudocolor).
Direct IF Protocol Using Antibodies Conjugated to Different Fluorophores
Below is a general protocol overview for direct IF staining using antibodies directly conjugated to different fluorophores. Note that the actual protocol will vary based on the specific products’ recommended protocol.
- Fixation / permeabilization
- Optimize protocol for best results with both antibodies
- Separate testing may be required
- Rinse
- Dilute each antibody to its recommended dilution in antibody dilution buffer; incubate overnight at 4°C
- Rinse
- Perform any counterstaining steps using complementary reagents, mount in anti-fade reagent
The pros and cons of using a direct method of IF staining and antibodies conjugated to different fluorophores are as follows:
Pros:
- Allows for multiplexing of antibodies raised in the same host species
- More efficient than indirect detection (no secondary detection step)
- Similar to standard staining protocols (Immunofluorescence Protocol with Formaldehyde Fixation)
- Utilizes common reagents and doesn’t require special imaging equipment
Cons:
- Dimmer than indirect detection using secondary antibodies
- Limited to available fluorophores
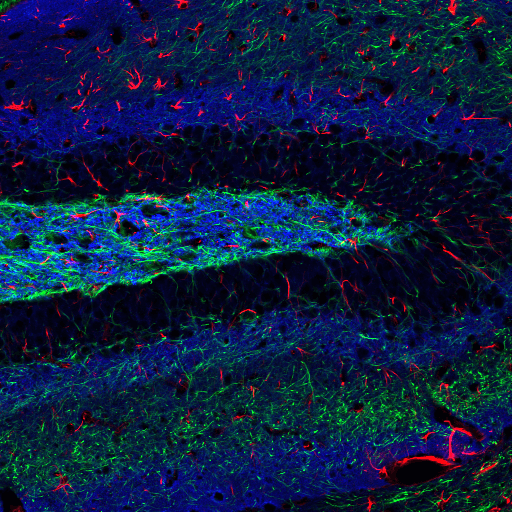 Adult rat hippocampus stained with Neurofilament-L (C28E10) Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) #8024 (green), GFAP (GA5) Mouse mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) #3656 (red), and α-Synuclein (D37A6) XP® Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) #4639 (blue pseudocolor).
Adult rat hippocampus stained with Neurofilament-L (C28E10) Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) #8024 (green), GFAP (GA5) Mouse mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) #3656 (red), and α-Synuclein (D37A6) XP® Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) #4639 (blue pseudocolor).