Biological research is about expanding knowledge, so it's not uncommon for scientists to study proteins for which antibodies have not yet been developed. How then, can mechanistic studies be performed for these novel or less-characterized proteins?
Epitope tagging is a powerful tool for such protein studies, and can be used in myriad experimental applications. However, care must be taken not only in choice of epitope tag, but in selection and validation of the antibodies used.
What is epitope tagging?
Epitope tagging is a technique where a known epitope, consisting of a few amino acids, is fused to a recombinant protein using genetic engineering. The epitope tag can be recognized by antibodies, and therefore, the technique can be used for labeling and detection of proteins in immunoassays. It is especially useful when studying newly discovered proteins to which antibodies are not yet available, proteins that generate a poor immune response, or low-abundance proteins.
Popular tags include FLAG, 6xHistidine (His), and Myc tag. The addition of an epitope tag should always be optimized based on the protein in question, which includes stringent experimental design and confirmation to ensure the epitope fusion will not interfere with protein structure, stability, or function.
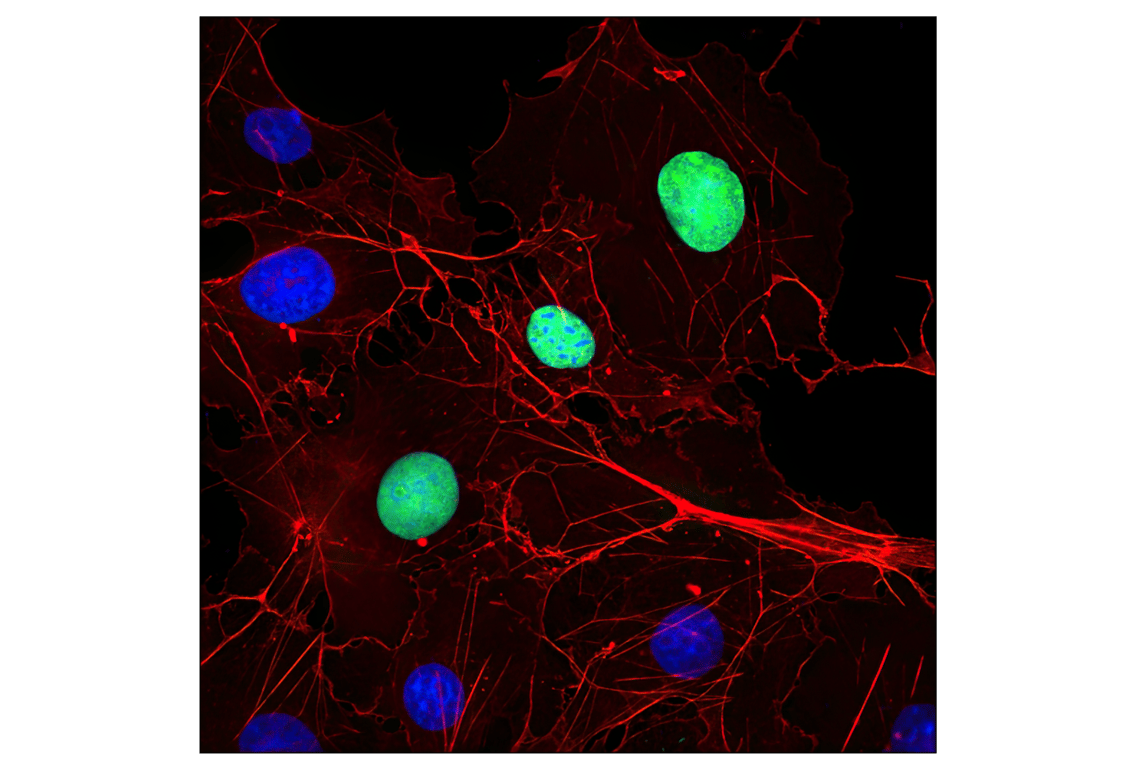
Immunofluorescent analysis of COS cells transfected with a Myc-tagged protein using Myc-Tag (9B11) Mouse mAb #2276 (green). Actin filaments were labeled with DyLight™ 554 Phalloidin #13054 (red). Blue pseudocolor = DRAQ5® #4084 (fluorescent DNA dye).
The addition of an epitope tag should always be optimized based on the protein in question, which includes stringent experimental design and confirmation to ensure the epitope fusion will not interfere with protein structure, stability, or function.
However, validation of a new epitope-tagged protein should also consider the accessibility of the tag, as they must operate within the context of the protein they are fused with. As such, the surrounding protein environment likely influences the interaction between antibodies and epitopes. Epitopes may be fused to the N- or C-terminus or even inserted into internal open reading frames (ORF) when tagging at either terminus is not functionally available for the protein in question.
Therefore, surrounding amino acids may affect antibody functionality in context-specific ways.
Myc-Tag (9B11) Mouse mAb #2276 Is a Superior Clone Against Top-cited Myc-tag Competitor
Recently, authors of an article in Science Signaling investigated the effects of a Myc tag insertion location on antibody function. Their efforts focused on the most cited antibody for Myc, monoclonal antibody 9E10. Schüchner et al., found that 9E10 performance in western blots was greatly reduced when the Myc tag sequence was followed by smaller, neutral amino acids rather than a series of positively charged amino acids.
This was compared to mouse Myc monoclonal clone 4A6 (Competitor A), which showed much more consistent detection of the Myc-tagged protein despite changes in the neighboring amino acid sequences. Researchers further investigated these effects by performing a microarray analysis to examine all 20 proteinogenic amino acids at each of the four positions C-terminal to the epitope tag. Compared to an alternative monoclonal antibody, 9E10 was vastly more sensitive to sequence location and context. Signal variability for 9E10 was extremely high, with signal for 19 peptides below 10% of the average signal, and five peptides not detected by 9E10 at all. Researchers then carried out double-substitutions of amino acids in positions +1 and +2 of the Myc tag, and again compared 9E10 to the alternative 4A6 antibody. They found that 9E10 now failed to detect 20 peptides, whereas the 4A6 antibody did not fail to detect any. This clearly demonstrates that the protein coding sequence immediately surrounding the epitope is critical for 9E10 reactivity.

Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded COS cell pellets, control (upper) or transfected with a carboxy-terminal Myc tagged protein (lower), using Myc-Tag (9B11) Mouse mAb.
To assess if this context-dependent sequence sensitivity is common, researchers then turned their focus to additional popular Myc antibodies, which they analyzed by western blot. Included amongst these antibodies were mouse monoclonal clone 9E10 (Competitor A), monoclonal clone 4A6 (Competitor A), and mouse monoclonal clone 9B11 (Cell Signaling Technology), so chosen due to their number of citations, availability, and host animal. The Myc epitope was fused in four different contexts - either to the N- or C-terminus of a fragment of rat PP2A B55α, with the immediate up- or downstream sequence comprised of seven amino acids derived from popular mammalian expression vectors. These were compared to mouse monoclonal antibody clone 2G9 for B55α. The authors found that many popular Myc antibodies showed considerable variability in the ability to detect the four tagged proteins, unsurprisingly including 9E10. Notably, 9B11 was one of only two antibodies that demonstrated consistency in the detection of all four Myc-tagged proteins, suggesting that this antibody is comparatively insensitive to local amino acid sequence environment.
Learn more about Myc-Tag (9B11) Mouse mAb.
Epitope Tagging: Context Matters
While it remains true that epitope-tagging is an essential tool for researchers, this work shows that care must be taken not only in choice of epitope tag, but in selection and validation of the antibodies used to detect them. While mouse monoclonal clone 9E10 is by far the most heavily utilized and cited antibody, this work demonstrates that it is highly susceptible to inhibition due to immediately adjacent amino acid sequence.
Therefore, researchers will want to carefully consider antibodies for their specific application, and likely focus on readily available commercial alternatives that do not demonstrate the same context-specific sensitivity.
Explore epitope tags from CST:
References
- P. Hopp, K. S. Prickett, V. L. Price, R. T. Libby, C. J. March, D. P. Cerretti, D. L. Urdal, P. J. Conlon, A Short polypeptide marker sequence useful for recombinant protein identification and purification. Bio/Technology 6, 1204–1210 (1988).
- Hochuli, W. Bannwarth, H. Döbeli, R. Gentz, D. Stüber, Genetic approach to facilitate purification of recombinant proteins with a novel metal chelate adsorbent. Bio/Technology 6, 1321–1325 (1988).
- I. Evan, G. K. Lewis, G. Ramsay, J. M. Bishop, Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol. Cell. Biol. 5, 3610–3616 (1985).
- E. Zordan, B. J. Beliveau, J. A. Trow, N. L. Craig, B. P. Cormack, Avoiding the ends: Internal epitope tagging of proteins using transposon Tn7. Genetics 200, 47–58 (2015).